Online NVR Tests for 11 Plus Non-Verbal Reasoning
Visuteach provides an interactive online GL Assessment 11 plus non-verbal reasoning (NVR) membership package which helps prepare for GL Assessment 11 plus non-verbal reasoning (NVR) entrance exams and admissions assessments for grammar schools, independent schools and private schools. The online 11 plus non-verbal reasoning membership package contains three sixty question multiple-choice GL Assessment style non-verbal reasoning (NVR) tests. Each test should be completed in thirty minutes. Our 11 plus non-verbal reasoning questions are similar to, and based upon, the questions in the official GL Assessment familiarisation practice paper packs which are sold online and in shops. Our tests are online multiple-choice tests with automatic and immediate marking.
This page contains demo computer software tests of our online 11 plus GL Assessment non-verbal reasoning (NVR) membership package for grammar school, independent, private school and secondary school entrance exams. You can download a pdf file of a sample 11 plus non verbal reasoning test, and answers to the sample test questions are shown further down this web page.
Video Explanations for Some Non-Verbal Reasoning Questions
GL Assessment Non-Verbal Reasoning 11 Plus Demo Tests
The untimed test has answers immediately after each question, the timed test has answers at the end of the test.
11 Plus Non-Verbal Reasoning (NVR) Sample Test
You can download and print out a pdf file of Visuteach’s sample non-verbal reasoning (NVR) test by clicking on the link below:
11 Plus Non-Verbal Reasoning Sample Test
Alternatively, you can open the 11 plus non-verbal reasoning sample test below. The sample test below can be displayed in full screen mode by clicking on the Full Screen icon (which has has four small white diagonal arrows) on the toolbar at the bottom of the passage. To exit from full screen mode, you can click on the Full Screen icon or press the Esc key on your keyboard.
For mobile users, you can use pinch and zoom to enlarge the text.
The answers to the NVR sample test are shown in the tabs below.
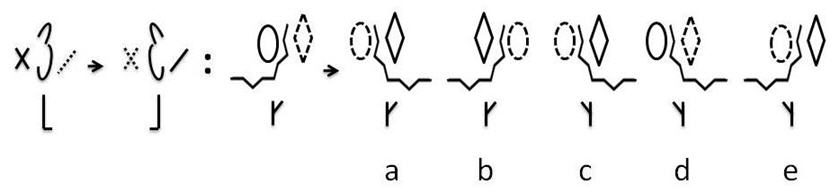
To get to the second pattern from the first pattern, the middle shape of the top row of the first pattern and the shape underneath it are flipped to the right. Then the first and third shapes of the top row reverse their outlines (i.e. the solid lines become dashed and the dashed lines become solid). Applying the same operations to the third pattern results in answer c.
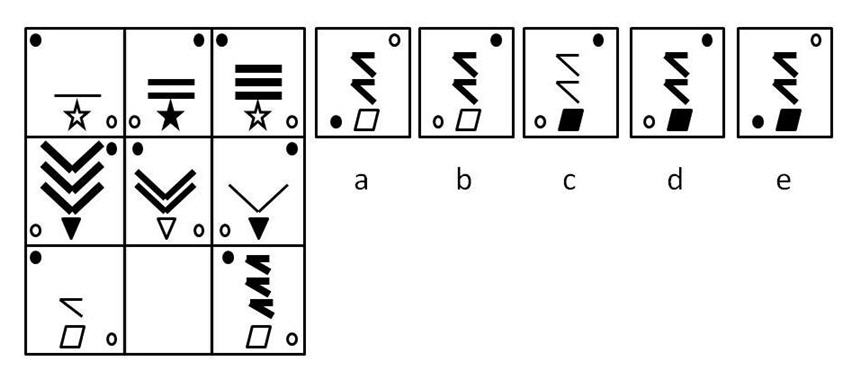
Within a row, each box contains two diagonally placed circles, the bottom one white and the top one black. These circles change their diagonal orientation between boxes (i.e. changing from top left, bottom right to bottom left, top right). Each box also contains a symbol at the bottom which alternates between white and black. Within each row, each box also contains a pattern which appears once, twice or three times, and the thickness of the pattern varies from thin to medium to thick between boxes. The empty box must therefore contain the pattern in d.
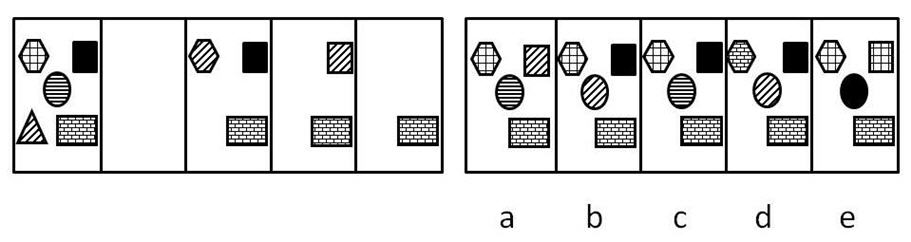
As we move between boxes from left to right, the shape with the diagonal stripes is removed from its current box. The diagonal stripes are then transferred to one of the other shapes (i.e. the shape changes its shading to a diagonal striped shading) and this shape then becomes the next shape to be removed. The empty box therefore contains the pattern in b.
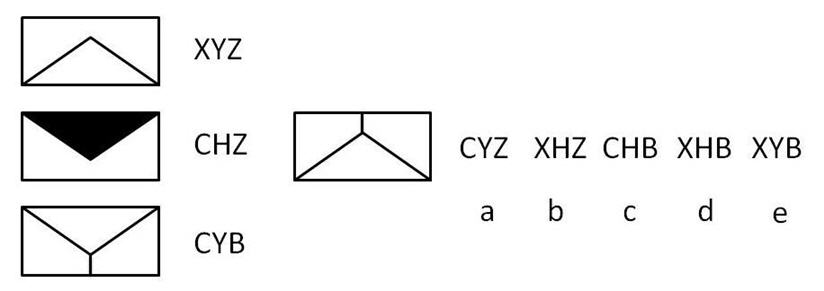
The first letter represents the direction of the pattern (C is upwards, with the triangle at the top, X is downwards, with the triangle at the bottom). The second letter represents the colour of the triangle (Y is white, H is black). The third letter represents the number of internal lines in the pattern (Z is 2, B is 3). The pattern to the left of the codes is in a downwards position (so its first letter is X), has a white triangle (so its second letter is Y) and has three internal lines (so its third letter is B). Therefore its code is XYB and the answer is e.
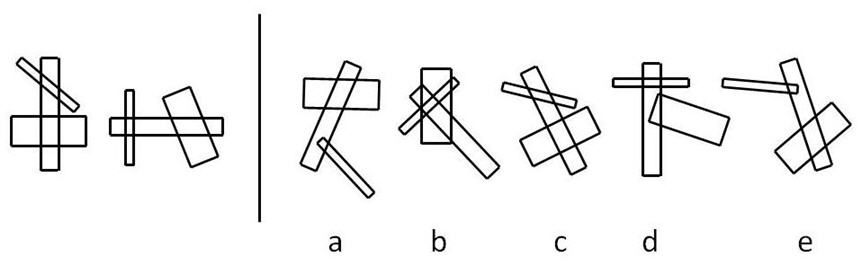
Each of the two patterns on the left has a medium width rectangle which has two of its sides crossed by each of the other two rectangles and these two rectangles do not cross each other. Also one of the two rectangles must cross the medium width rectangle at right angles. The most like pattern is therefore c.
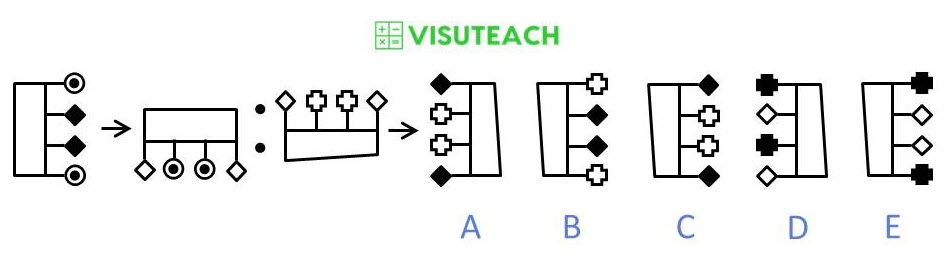
The figure is rotated 90 degrees clockwise, the outer two poles are moved to the inner two pole positions and the inner two poles are moved to the outer two pole positions and the colours of their two end shapes are inverted (i.e. if they are white they become black and vice versa).
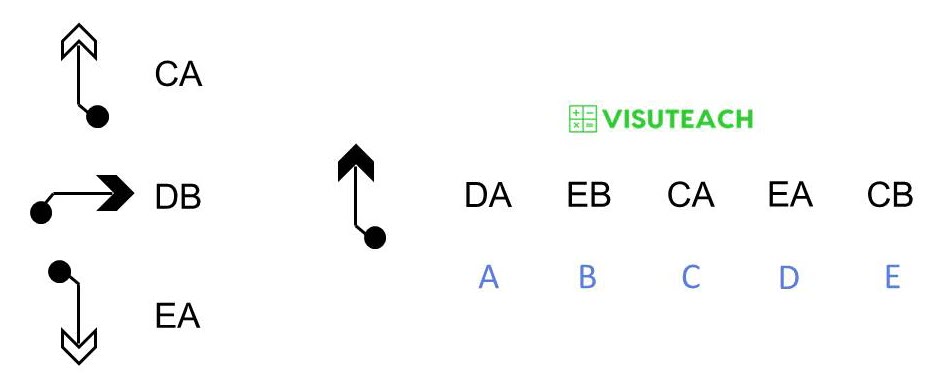
Two figures have A as the second letter, and what these two figures have in common (and how they differ from the other figure) is that they both have a white arrowhead. So A as a second letter means that the figure has a white arrowhead. Therefore, B as a second letter means that the figure has a black arrowhead.
None of the figures have the same first letter, so the first letters all represent something different i.e. they represent the direction of the arrow i.e. C means that the arrow points upwards, D means that the arrow points to the right and E means that the arrow points downwards.
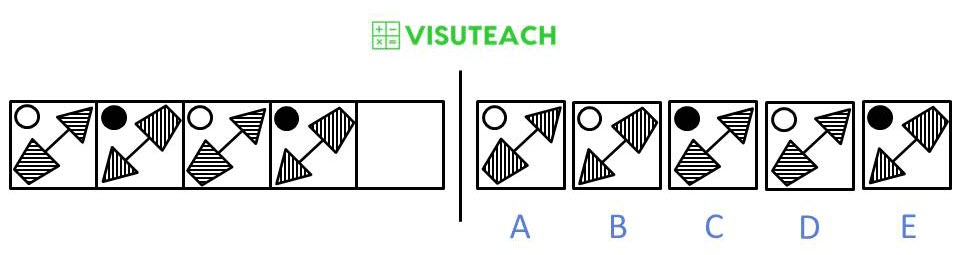
Moving from left to right, the circle changes colour from white to black, the joined figure is rotated 180 degrees and the shading of the figure changes from horizontal to vertical.
Alternatively, you can think of this as two alternating sequences with the same pattern in each sequence.
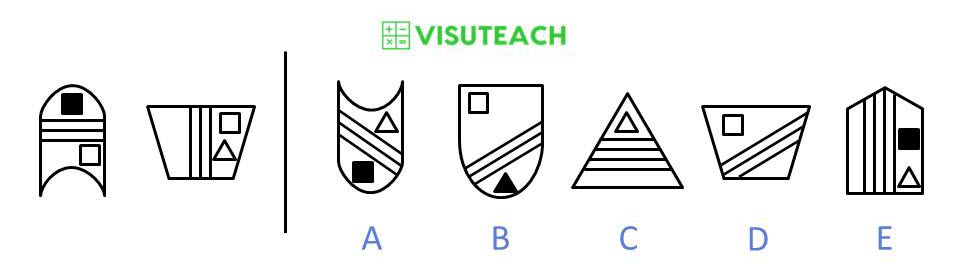
The two figures on the left have the following in common: each figure has 3 parallel lines inside it, and each figure contains two inner shapes, one of which is a white square.
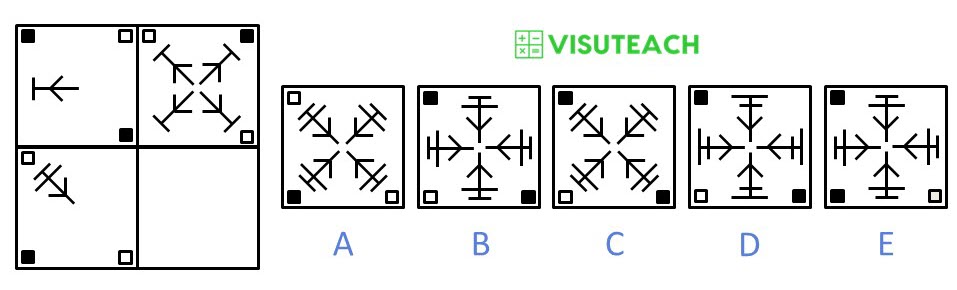
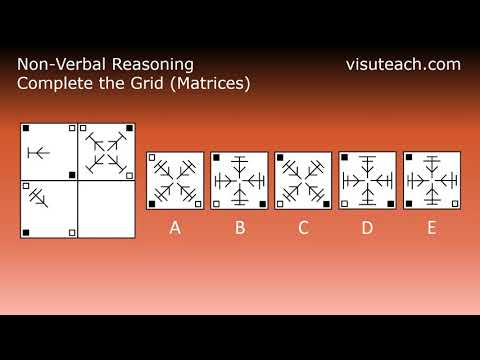
For each row, the small corner squares switch their colour from black to white and white to black, and the arrow shape is rotated 45 degrees clockwise and is then replicated three times at 90 degree intervals.
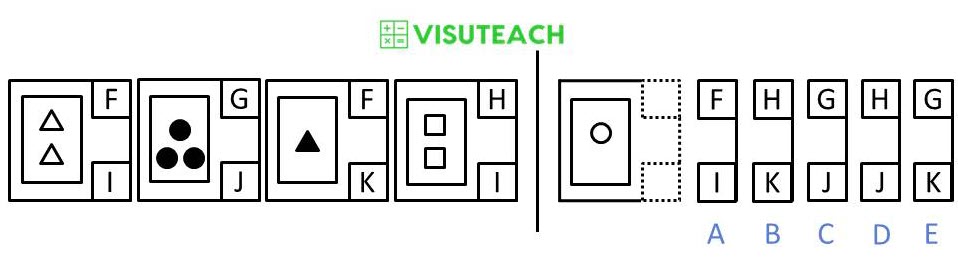
Two boxes contain the code F on the top, and what these two boxes have in common is that they contain a triangle. So the code on the top represents the type of shape within the large rectangle. The code F means that the shape is a triangle, the code G means that the shape is a circle, and the code H means that the shape is a square.
Two boxes contain the code I on the bottom, and what these two boxes have in common is that the large rectangle contains two shapes and that the shapes are white. So the code on the bottom must either represent the number of shapes or the colour of the shapes. It can’t mean the colour because the three black balls and the black triangle have different codes and yet they are both black. Therefore the code on the bottom must represent the number of shapes within the large rectangle. So the code I represents two shapes, the code J represents 3 shapes and the code K represents one shape.
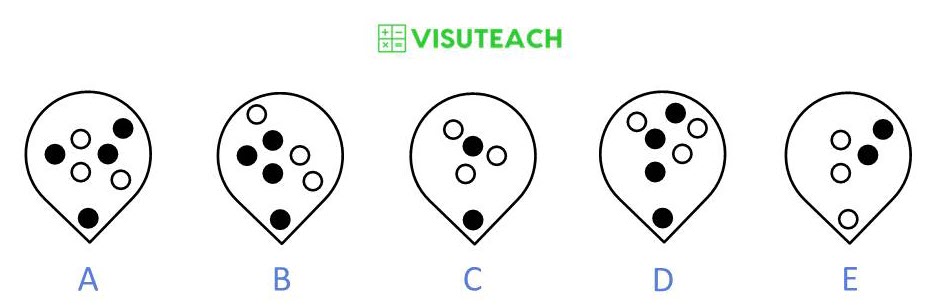
All of the figures, apart from E, have a black circle at the bottom of the shape.